Performance Improvement Vs Performance Optimization
Background
Recently I stumbled upon a tweet on my twitter timeline, that discussed about approaches / strategies that can be adopted to improve performance of enterprise applications. What struck me while going through its responses and various similar posts on Linkedin is - tons of material preaching and teaching of how to improve performance of a system is uni-dimensional. While I completely agree to the patterns / guidelines shared by our vibrant community, what IMO is getting missed out is fundamental understanding of Performance Engineering - Primary goal of Performance Engineering is to improve end user experience by reducing latency / increasing throughput. And during the course of improving end user experience it may even help in reducing computation cost - this is one of the most neglected part of running highly performant and optimal software systems. Hence I thought to pen down a brief write up to help us understand thin line of difference between Performance Improvement and Performance Optimization
I guess this article is going to be bit subjective. Hence please do expect some contradictions to your experiences and understanding - Its perfectly ok to disagree. So please don't hesitate sharing your disagreement in comments below :)
Performance Improvement (PI)
It is the science of making systems faster. While making systems run faster can be extremely contextual, below are the indicative list of areas that can be considered for improving performance of a system -
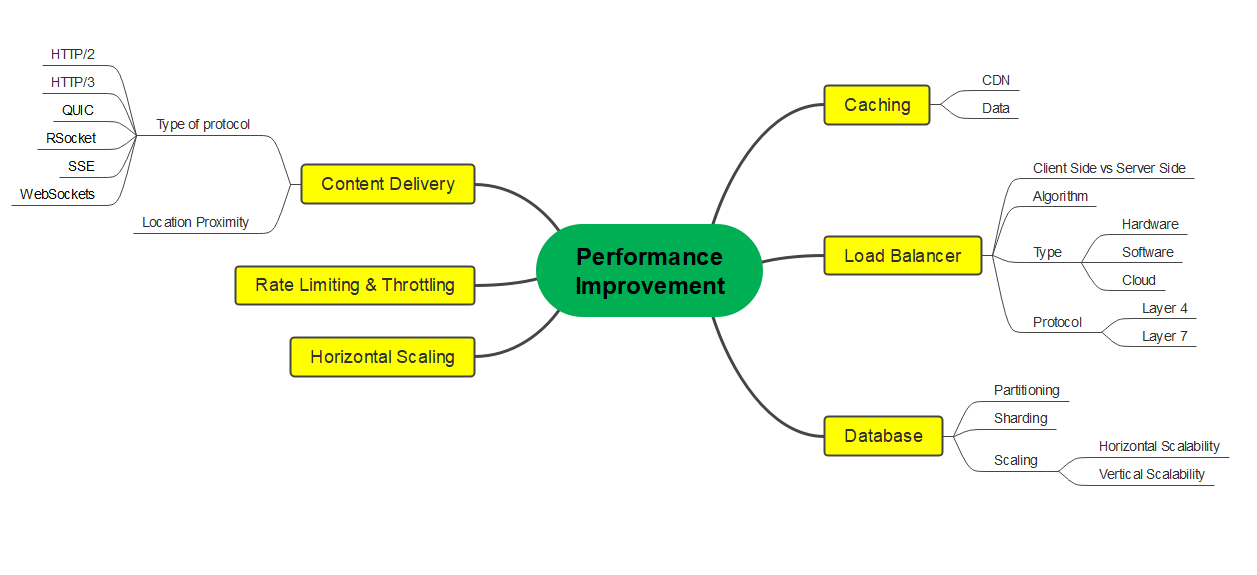
Load Balancing
- Considering nature of workload, load balancers can be selected based on its type i.e. Software / Hardware / Cloud and Protocol i.e. Layer 4 / Layer 7
- From performance improvement standpoint, its routing algorithm can be configured
Caching
- Adopting various data caching patterns (depending on underlying use cases) to avoid overloading databases
- Use CDNs to cache and server static assets; this will in turn reduce load on your system
Database
- Partitioning can help improve query performance by reducing amount of data that needs to be scanned
- Sharding can help distribute your data across multiple database instances. Each shard handles portion of data, which can lead to better parallelism and thereby improved performance. This in turn adds complexity to your systems architecture.
Content Delivery
- Use appropriate CDNs to distribute content geographically and thereby reduce latency for users accessing your system from different regions
Rate limiting and Throttling
- Implement rate limiting to control the number of requests a client can make in a given time-frame
- Use request throttling to smooth out traffic spikes
Horizontal Scaling
- Performance can be improved by adding more servers or instances to your application
Performance Optimization (PO)
It is the science of making systems efficient. Going by dictionary meaning of optimization -
The action of making the best or most effective use of a situation or resource
This would entail deep inspection and understanding of software systems from coding, business and architecture standpoint. Based on my limited experience below are the indicative list of areas that can be considered from Performance Optimization standpoint -
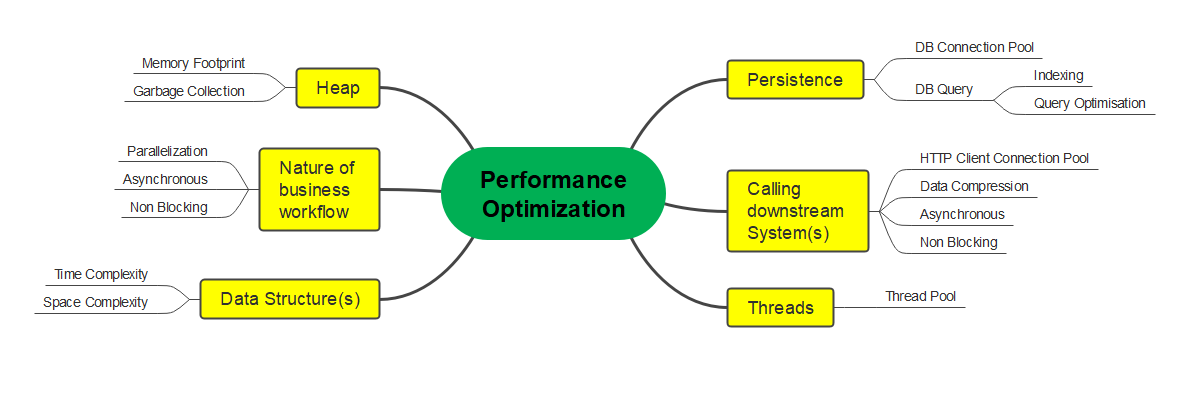
Persistence
- One of the most common performance hot spot, which when optimized can lead to significant performance gains
- Optimal configuration of Database connection pool
- Adding appropriate index based on lookup operations
- Optimizing query by understanding its explain plan
Calling downstream systems
- Optimal configuration of HttpClient connection pool - RestTemplate / WebClient
- Compressing request / response data using techniques like ProtoBuf / GZIP to reduce bandwidth usage and improve latency
Multi-Threading
- Maintaining dedicated thread pools along with required configurations for multi threaded and asynchronous workflows
Heap
- Tracking memory footprint and understanding projected workload can help us understand probable memory hot spots
- Garbage Collection events : One of the most overlooked and under rated area from performance optimization and analysis standpoint. It can have major ramifications considering CPU utilization and latency numbers
Nature of business workflow
This would mainly govern software architecture of the application. It in a way will help us determine whether the workflow can be realized with Parallel vs Asynchronous Vs Non Blocking implementation
Data Structures
Judicious selection of data structures is of paramount importance, as it can have significant impact on memory footprint and latency.
Conclusion
Both of the above aspects of Performance Engineering i.e. Performance Improvement (i.e. PI) and Performance Optimization (i.e. PO) are interrelated and are even used interchangeably. One needs to be mindful about the subtle differences between them and accordingly adopt either / both of them depending on system's need. Generally speaking, PI may provide certain solutions that would encompass software, hardware and infrastructure. It may even increase overall cost of running systems. PO in my understanding would primarily be scoped within the purview of software application. And hence PO would generally ensure that systems along with their constraints are functioning in most effective manner. Generally speaking, PO would most probably not increase systems operational cost.
In nutshell, Performance Engineering is one of the most important NFR for distributed systems. Considering its significance, we as software engineers should not just narrow down to _Performance Improvement only. We should also consider Performance Optimization. Personally speaking, I would most likely start with Performance Optimization and than follow it up with Performance Improvement - as it would not only ensure reduced latency / higher throughput but it may also help in reducing cost of computation, which would bring down my cloud bill!
comments powered by Disqus